Everything You Should Know About Ear Infections in Adult
Ear infections can affect different parts of the ear and may be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. The recommended treatment can vary based on the type of ear infection and the specific cause.
Adult ear infections
Ear infections may be more common in children than in adults, but adults are still susceptible to these infections. Unlike childhood ear infections, which are often minor and pass quickly, adult ear infections can sometimes signal a more serious health problem.
If you’re an adult with an ear infection, it’s a good idea to pay close attention to your symptoms and talk with your doctor.
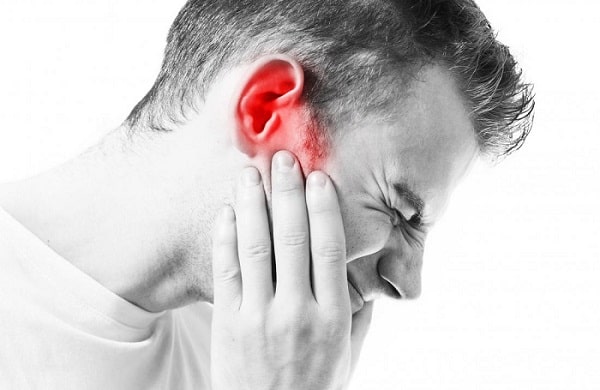
Symptoms
There are three main types of ear infections. They correspond to the three main parts of the ear: inner, middle, and outer.
Inner ear infection
A condition diagnosed as an inner ear infection may actually be a case of inflammation and not an actual infection. In addition to ear pain, symptoms include:
• dizziness
• nausea
• vomiting
• vertigo
• sudden hearing loss
Rarely, inner ear trouble may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as meningitis.
Middle ear infection
The middle ear is the area right behind your eardrum.
A middle ear infection is also known as otitis media. It’s caused by fluid trapped behind the eardrum, which causes the eardrum to bulge. Along with an earache, you may sense fullness in your ear.
Otitis media can come with a fever. You may also have trouble hearing until the infection starts to clear.
If you experience fluid draining from your ear, it could be a sign the middle ear infection has progressed to a tympanic membrane rupture. This condition can cause a sudden loss of hearing, but tends toTrusted Source heal on its own.
Outer ear infection
The outer ear is that part of your ear that extends out from your eardrum to the ear opening.
An outer ear infection is also known as otitis externa. An outer ear infection often starts as an itchy rash. The ear may become:
• painful
• tender
• red
• swollen
Causes
Ear infections can be caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. But whether you get an outer or middle ear infection depends on how you become infected.
Middle ear infection
A middle ear infection often starts from a cold or other respiratory problem. The infection moves to one or both ears through the eustachian tubes. These tubes regulate air pressure inside your ear. They connect to the back of your nose and throat.
An infection can irritate the eustachian tubes and cause them to swell. Swelling can prevent them from draining properly. When fluid inside these tubes can’t drain, it builds up against the eardrum.
Outer ear infection
An outer ear infection is sometimes called swimmer’s ear. That’s because it often starts as a result of water that remains in the ear after swimming or bathing. The moisture becomes a breeding ground for bacteria.
If your outer ear is scratched or if you irritate the outer lining of your ear by putting your fingers or other objects in your ear, a bacterial infection can occur.
Risk factors
One of the reasons children are more likely than adults to get ear infections is that their eustachian tubes are smaller and more horizontal than the tubes in most adults. If you have small eustachian tubes or you have tubes that haven’t developed more of a slope, you’re at a higher risk for developing an ear infection.
You may also be more likely to get an ear infection if you smoke or are around a lot of secondhand smoke.
Having seasonal allergies or year-round allergies also puts you at risk.
Developing a cold or an upper respiratory infection also increases your risk.




ارسال دیدگاه
مجموع دیدگاهها : 0در انتظار بررسی : 0انتشار یافته : ۰